Correct answer for all Question is A
76). A 60-year-old woman, mother of 6 children, developed a sudden onset of upper abdominal
pain radiating to the back, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever and chills. Subsequently,
she noticed yellow discoloration of her sclera and skin. On physical examination the patient was
found to be febrile with temp of 38, 9oC, along with right upper quadrant tenderness. The most
likely diagnosis is
A. Choledocholithiasis
B. Benign biliary stricture
C. Malignant biliary stricture
D. Carcinoma of the head of the pancreas
E. Choledochal cyst
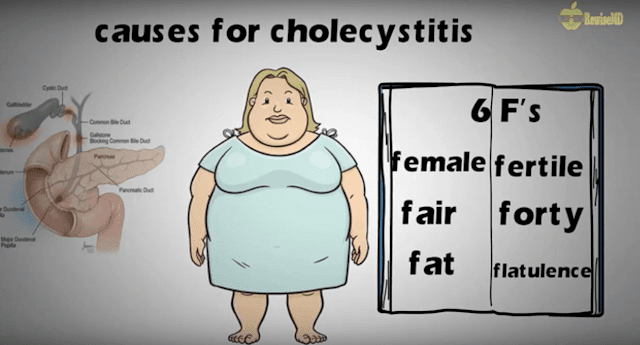
Explanation: 5F are to risk factors for the development of cholelithiasis in an event of upper abdominal pain:
Fair: more prevalent in Caucasian population(fair)
Fat: BMI >30
Female gender
Fertile: one or more children
Forty: age ≥40
77). A 45-year-old woman, mother of four children, comes to the emergency room complaining
of a sudden onset of the epigastric and right upper quadrant pain, radiating to the back,
accompanied by vomiting. On examination, tenderness is elicited in the right upper quadrant,
bowel sounds are decreased, and laboratory data shows leukocytosis, normal serum levels of
amylase, lipase, and bilirubin. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Acute cholecystitis
B. Perforated peptic ulcer disease
C. Myocardial infarction
D. Sigmoid diverticulitis
E. Acute pancreatitis
78). During an operation for presumed appendicitis the appendix was found to be normal;
however, the terminal ileum is evidently thickened and feels rubbery, its serosa is covered with
grayish-white exudate, and several loops of apparently normal small intestine are adherent to
it. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Crohn’s disease of the terminal ileum
B. Perforated Meckel’s diverticulum
C. Ulcerative colitis
D. Ileocecal tuberculosis
E. Acute ileitis
Explanation:Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus.Mostly affected in crohn's disease is terminal ileum.
79). A female patient has been suffering from pain in the right subcostal area, bitter taste in the
mouth, periodical bile vomiting for a month. The patient put off 12 kg. Body temperature in the
evening is 37, 6oC. Sonography revealed that bile bladder was 5,5х2,7 cm large, its wall - 0,4
cm, choledochus - 0,8 cm in diameter. Anterior liver segment contains a roundish hypoechoic
formation up to 5 cm in diameter and another two up to 1,5 cm each, walls of these formations
are up to 0,3 cm thick. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Alveolar echinococcus of liver
B. Liver cancer
C. Liver abscess
D. Cystous liver cancer
E. Paravesical liver abscesses
Explanation: Echinococcosis, also called hydatid disease, It is a parasitic disease of tapeworms of the Echinococcus type. The two main types of the disease are alveolar echinococcosisand cystic echinococcosis . USG show multiple hypo-echoic cyst like formation.
80). In autumn a 25-year-old patient developed stomach ache arising 1,5-2 hours after having
meals and at night. He complains of pyrosis and constipation. The pain is getting worse after
consuming spicy, salty and sour food, it can be relieved by means of soda and hot-water bag.
The patient has been suffering from this disease for a year. Objectively: furred moist tongue.
Abdomen palpation reveals epigastrial pain on the right, resistance of abdominal muscles in the
same region. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Duodenal ulcer
B. Chronic cholecystitis
C. Diaphragmatic hernia
D. Stomach ulcer
E. Chronic pancreatitis
Explanation: Duodenal ulcer is associated stomach pain that arose 1.5-2.5 hours after having meal and get relief by meal. Spring and autumn are environmental risk factor for duodenal ulcer.
81). 4 hours after having meals a patient with signs of malnutrition and steatorrhea experiences
stomach pain, especially above navel and to the left of it. Diarrheas take turns with constipation
lasting up to 3-5 days. Palpation reveals moderate painfulness in the choledochopancreatic
region. The amylase rate in blood is stable. X-ray reveals some calcifications located above
navel. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Chronic pancreatitis
B. Chronic gastroduodenitis
C. Duodenal ulcer
D. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
E. Chronic calculous cholecystitis
Explanation: Chronic pancreatitis leads to Deficiency of pancreatic enzyme (lipase) which is essential for conversion of triglyceride to monoglycerides and free fatty acids which is absorbed. Due to lipase deficiency cause natural fat in stool i.e steatorrhea. X-ray reveals calcifications above naval is pathognomonic sign.
82). A 51-year-old female patient complains of frequent defecation and liquid blood-streaked
stools with mucus admixtures, diffuse pain in the inferolateral abdomen, 6 kg weight loss over
the previous month. Objectively: body temperature - 37, 4oC, malnutrition, skin is pale and dry.
Abdomen is soft, sigmoid is painful and spasmodic, makes a rumbling sound. Liver is dense,
painful, extends 3 cm below the costal margin. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Non-specific ulcerative colitis
B. Bacillary dysentery
C. Sprue
D. Intestinal enzymopathy
E. Helminthic invasion
Explanation: Nonspecific ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the colon and rectum , which develops starting from the rectum. Usually, the periods of exacerbation of ulcerative colitis alternate with the absence of its evident symptoms.
83). A 50-year-old patient complains about having pain attacks in the right subcostal area for
about a year. He pain arises mainly after taking fattening food. Over the last week the attacks
occurred daily and became more painful. On the 3rd day of hospitalization the patient
presented with icteritiousness of skin and scleras, lightcolored feces and dark urine. In blood:
neutrophilic leukocytosis - 13, 1 · 109/l, ESR- 28 mm/h. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Chronic calculous cholecystitis
B. Chronic recurrent pancreatitis
C. Fatty degeneration of liver
D. Chronic cholangitis, exacerbation stage
E. Hypertensive dyskinesia of gallbladder
Explanation: lightcolored feces and dark urine indicate obstructive jaundice(icteritiousness of skin and scleras). Increase ESR and leucocytosis indicate inflammation. Right subcostal pain for one year it means chronic.
84). A 6-year-old child has duodenal ulcer. What antibacterial drug should be coadministered
together with metronidazole and De-Nol in order to eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection?
A. Amoxicillin
B. Tetracycline
C. Oleandomycin
D. Biseptol
E. Sulfadimethoxinum
Explanation: Triple therapy = PPI, Amoxycillin, clarithromysin.
Quadraple therapy: Bismuth(De-nol), ppI, metronidazole, tetracycline.
Note: Amoxicillin is given with metronidazole and denol along with PPI.
85). A 35-year-old patient complains of heartburn, sour eructation, burning, compressing
retrosternal pain and pain along the esophagus rising during forward bending of body. The
patient hasn’t been examined, takes Almagel on his own initiative, claims to feel better after its
taking. Make a provisional diagnosis:
A. Gastroesophageal reflux disease
B. Functional dyspepsia
C. Cardiospasm
D. Gastric ulcer
E. Duodenal ulcer
Explanation: Main feature of Gastroesophageal reflux is substernal pain during swallowing which is aggravated during bending forward. Heartburn due to acid reflux.
86). A patient complains of retrosternal pain, difficult swallowing, over 10 kg weight loss within
three months, general weakness. In blood: hypochromic anaemia, neutrophilic leukocytosis. In
feces: weakly positive Gregersen’s reaction. On esophagram a filling defect with ill-defined
serrated edges shows up along a large portion of the esophagus. What is the most likely
diagnosis?
A. Esophageal carcinoma
B. Benign tumour
C. Esophageal achalasia
D. Peptic ulcer
E. Sideropenic dysphagia
Explanation: sudden weight loss is alarm sign of cancer and patient have difficult in swallowing, esophagram show ill defined edge indicate esophageal cancer.
87).A 13-year-old girl has a 5-year history of pain in the right hypochondrium irradiating to the right
shoulder blade. The pain attacks are usually associated with diet violations, they are short and can be
easily relieved by antispasmodic drugs. During a pain attack, palpation of the abdomen is painful, the
pain is most intensive in the projection of the gallbladder. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Biliary dyskinesia
B.Chronic cholecystitis
C.Chronic gastroduodenitis
D.Chronic pancreatitis
E.Duodenal ulcer
Explanation: Biliary dyskinesia is a motility disorder that affects the gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi. The motility disorder of the gallbladder is called gallbladder dyskinesia. antispasmodic drug relief the pain.
88).A 48-year-old male patient complains of constant pain in the upper abdomen, mostly on the left, that is getting worse after taking meals; diarrhea, weight loss. The patient is an alcohol abuser. 2 years ago he had acute pancreatitis. Blood amylase is 4 g/h·l. Coprogram shows steatorrhea, creatorrhea. Blood glucose is 6,0 mmol/l. What treatment is indicated forth is patient?
A.Panzinorm forte
B.Insulin
C.Gastrozepin
D.Contrycal
E.No-spa
Explanation :This patient suspect to have chronic pancreatitis because history of acute pancreatitis and coprogram show steatorrhea so pancreatic enzyme(panzinorm forte) should be replaced.
89).A 24-year-old female patient complains of pain in the right hypochondrium that is getting worse after taking meals; nausea, fever up to37,7oC, icteric skin, pain in the large joints. These presentations have been observed for 8 months. Objectively: hepatosplenomegaly. Blood test results: ESR- 47 mm/h, total bilirubin - 86,1 mmol/l, direct bilirubin - 42,3 mmol/l. Total protein - 62 g/l, albumins - 40%, globulins - 60%, gamma globulins - 38%. Viral hepatitis markers were not detected. The antibodies to smooth muscle cells are present. On ultrasound the portal vein diameter was of 1 cm. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Autoimmune hepatitis
B.Primary biliary cirrhosis
C.Gilbert’s syndrome
D.Cholangiogenic hepatitis
E.Hemachromatosis
Explanation: Antibodies to smooth muscle cells specific for Autoimmune hepatitis.
90). A 57-year-old female complains of having a sensation of esophageal compresion, palpitation, difficult breathing during eating solid food, occasional vomiting with a full mouth, "wet pillow"sign at night for the last 6 months. Objectively: body tempearture -39 oC, height - 168 cm, weight - 72 kg, Ps- 76/min, АP- 120/80 mm Hg. X-ray revealed a considerable dilation of esophagus and its constriction in the cardial part. What pathology is most likely to have caused dysphagia in this patient?
A.Achalasia cardiae
B.Primary esophagism
C.Hiatal hernia
D.Esophageal carcinoma
E.Reflux esophagitis
Explanation: Achalasia is a condition in which the muscles of the lower part of the oesophagus fail to relax, preventing solid and liquid food from passing into the stomach. Bird beak or rat tail (esophageal dilatation with level of fluid ) radiological sign is specific for achalasia.
91). A 64-year-old patient has been referred to planned hospitalization for general weakness, poor appetite, progressive jaundice which appeared over 3 weeks ago and wasn’t accompanied by pain syndrome. Objectively: body temperature is at the rate of 36,8oC,Ps-78/min, abdomen is soft and painless, the symptoms of peritoneal irritation are present, palpation reveals a dramatically enlarged, tense gallbladder. What disease are these symptoms typical for?
A.Cancer of the pancreatic head
B.Duodenal ulcer
C.Acute cholecystitis
D.Chronic cholecystitis
E.Lamblia-induced cholecystitis
Explanation: Elderly is risk factor. weight is alarm sign for cancer. enlarged, tense gallbladder due to bile outflow obstruction by pancreatic head cancer.
92).A patient is 31 years old. Double-contrast barium swallow revealed a filling defect on the posterior wall in the middle segment of esophagus. The defect looked like a well-defined oval 1,8x1,3 cm large. Mucosal folds adjacent to the defect were intact, peristalsis and elasticity of the walls remained unchanged. Digestive tract problems were absent. What is the provisional diagnosis?
A.Esophageal tumour
B.Achalasia cardia
C.Esophageal burn
D.Diverticulum
E.Barrett’s esophagus
Explanation :- Double-contrast barium swallow revealed a filling defect on the posterior wall in the middle segment of esophagus and well defined oval mass indicate esophageal tumor.
93). A 28-year-oldmale patient complains of regurgitation, cough and heartburn that occurs every day after a meal, when bending forward or lying down. These problems have been observed for 4 years. Objective status and laboratory values are normal. FEGDS revealed endoesophagitis. What is leading
factor in the development of this disease?
A.Failure of the inferior esophageal sphincter
B.Hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid
C.Duodeno-gastric reflux
D.Hypergastrinemia
E.Helicobacter pylori infection
Explanation: patient had specific character of GERD(Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive disease. GERD occurs when stomach acid or, occasionally, stomach content, flows back into food pipe (esophagus) and reflux irritates the lining of esophagus and causes GERD)
94).A 33-year-old female complains of escalating spastic pain in the abdomen after the psycho-emotional stress. The patient has intermittent bowel movements, that is 2-3 bowel movements after waking up alternate with constipation lasting for 1-2 days. Objectively: body weight is unchanged, there is moderate pain on palpation of the sigmoid colon. Hb- 130 g/l, WBC-5,2· 109/l, ESR- 9mm/h. Proctosigmoidoscopy causes pain due to spastic bowel condition, intestinal mucosa is not changed. In the lumen there is a lot of mucus. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Irritable bowel syndrome
B.Crohn’s disease
C.Non-specific ulcerative colitis
D.Acute bowel ischemia
E.Malabsorption syndrome
Explanation : Diagnostic Criteria for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) :
1) Recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort at least 3 days/month in the last 3 months
Plus two or more of the following
2) Improvement with defecation
3) change in frequency of stool
4) change in stool form(appearance)
Note: There is no pathological changes in bowel.
95.A 44-year-old male patient complains of severe non-localized abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder girdle, repeated vomiting, red urine. The onset of the disease is associated with alcohol consumption. The face is hyperemic. AP- 70/40 mm Hg. Abdominal radiography reveals no pathological shadows. Hemodiastase is 54 mg/h/l. Prothrombin is 46%. What is the provisional diagnosis?
A.Acute pancreatitis
B.Acute myocardial infarction
C.Perforated gastric ulcer
D.Thrombosis of mesenteric vessels
E.Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta
Explanation: Acute pancreatitis is associated with alcohol consumption.
96).A 40-year-old male patient has had heaviness in the epigastric region for the last 6 months. He has not undergone any examinations. The night before, he abused vodka. In the morning there was vomiting, and 30 minutes after physical activity the patient experienced dizziness and profuse hematemesis. What pathology should be suspected in the first place?
A.Mallory-Weis’s syndrome
B.Menetrier’s disease
C.Gastric ulcer
D.Perforated ulcer
E.Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Explanation: Mallory-Weiss syndrome (MWS) is a condition marked by a tear in the mucous membrane, or inner lining, where the esophagus meets the stomach. It is mainly caused by severe repeated vomiting and alcoholism.
97).A 46-year-old male patient complains of periodic epigastric pain that occurs at night. Objectively: HR- 70/min, AP- 125/75 mm Hg, tenderness in the epigastric region is present. EGD confirms duodenal ulcer of 0,6 cm in diameter. Test for H. Pylori is positive. Which of the given antisecretory drugs will be a compulsory element of the treatment regimen?
A.Omeprazole
B.Famotidine
C.Pirenzepine
D.Atropine
E.Maalox
Explanation: Triple therapy = PPI(omeprazole), Amoxycillin, clarithromysin.
Quadraple therapy: Bismuth(De-nol), ppI, metronidazole, tetracycline.
98).A 49-year-old male patient complains of retrosternal pain, heartburn, weight loss of 8kg over the last year, constipation, weakness. The patient has been a smoker for 20 years, and has a 10-year history of Gastroesophageal reflux disease. The patient is asthenic, has dry skin. EGD revealed an ulcer in the lower third of the esophagus and esophageal stricture accompanied by edema, hyperemia and multiple erosions of the mucosa. What study is required for more accurate diagnosis?
A.Biopsy of the esophageal mucosa
B.X-ray examination of the esophagus
C.Respiratory test for Helicobacter pylori
D.pH-metry of the esophagus and the stomach
E.Fecal occult blood test
Explanation :- Above mentioned is elderly, smoker patient and have the history of GERD and there is loss of weight which is alarm sign for cancer. thus patient is suspected to have esophageal cancer because of esophageal erosion, stricture, edema. The best method of investigation in this case is Biopsy of the esophageal mucosa.
76). A 60-year-old woman, mother of 6 children, developed a sudden onset of upper abdominal
pain radiating to the back, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever and chills. Subsequently,
she noticed yellow discoloration of her sclera and skin. On physical examination the patient was
found to be febrile with temp of 38, 9oC, along with right upper quadrant tenderness. The most
likely diagnosis is
A. Choledocholithiasis
B. Benign biliary stricture
C. Malignant biliary stricture
D. Carcinoma of the head of the pancreas
E. Choledochal cyst
Explanation: 5F are to risk factors for the development of cholelithiasis in an event of upper abdominal pain:
Fair: more prevalent in Caucasian population(fair)
Fat: BMI >30
Female gender
Fertile: one or more children
Forty: age ≥40
77). A 45-year-old woman, mother of four children, comes to the emergency room complaining
of a sudden onset of the epigastric and right upper quadrant pain, radiating to the back,
accompanied by vomiting. On examination, tenderness is elicited in the right upper quadrant,
bowel sounds are decreased, and laboratory data shows leukocytosis, normal serum levels of
amylase, lipase, and bilirubin. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Acute cholecystitis
B. Perforated peptic ulcer disease
C. Myocardial infarction
D. Sigmoid diverticulitis
E. Acute pancreatitis
78). During an operation for presumed appendicitis the appendix was found to be normal;
however, the terminal ileum is evidently thickened and feels rubbery, its serosa is covered with
grayish-white exudate, and several loops of apparently normal small intestine are adherent to
it. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Crohn’s disease of the terminal ileum
B. Perforated Meckel’s diverticulum
C. Ulcerative colitis
D. Ileocecal tuberculosis
E. Acute ileitis
Explanation:Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus.Mostly affected in crohn's disease is terminal ileum.
79). A female patient has been suffering from pain in the right subcostal area, bitter taste in the
mouth, periodical bile vomiting for a month. The patient put off 12 kg. Body temperature in the
evening is 37, 6oC. Sonography revealed that bile bladder was 5,5х2,7 cm large, its wall - 0,4
cm, choledochus - 0,8 cm in diameter. Anterior liver segment contains a roundish hypoechoic
formation up to 5 cm in diameter and another two up to 1,5 cm each, walls of these formations
are up to 0,3 cm thick. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Alveolar echinococcus of liver
B. Liver cancer
C. Liver abscess
D. Cystous liver cancer
E. Paravesical liver abscesses
Explanation: Echinococcosis, also called hydatid disease, It is a parasitic disease of tapeworms of the Echinococcus type. The two main types of the disease are alveolar echinococcosisand cystic echinococcosis . USG show multiple hypo-echoic cyst like formation.
80). In autumn a 25-year-old patient developed stomach ache arising 1,5-2 hours after having
meals and at night. He complains of pyrosis and constipation. The pain is getting worse after
consuming spicy, salty and sour food, it can be relieved by means of soda and hot-water bag.
The patient has been suffering from this disease for a year. Objectively: furred moist tongue.
Abdomen palpation reveals epigastrial pain on the right, resistance of abdominal muscles in the
same region. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Duodenal ulcer
B. Chronic cholecystitis
C. Diaphragmatic hernia
D. Stomach ulcer
E. Chronic pancreatitis
Explanation: Duodenal ulcer is associated stomach pain that arose 1.5-2.5 hours after having meal and get relief by meal. Spring and autumn are environmental risk factor for duodenal ulcer.
81). 4 hours after having meals a patient with signs of malnutrition and steatorrhea experiences
stomach pain, especially above navel and to the left of it. Diarrheas take turns with constipation
lasting up to 3-5 days. Palpation reveals moderate painfulness in the choledochopancreatic
region. The amylase rate in blood is stable. X-ray reveals some calcifications located above
navel. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Chronic pancreatitis
B. Chronic gastroduodenitis
C. Duodenal ulcer
D. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
E. Chronic calculous cholecystitis
Explanation: Chronic pancreatitis leads to Deficiency of pancreatic enzyme (lipase) which is essential for conversion of triglyceride to monoglycerides and free fatty acids which is absorbed. Due to lipase deficiency cause natural fat in stool i.e steatorrhea. X-ray reveals calcifications above naval is pathognomonic sign.
82). A 51-year-old female patient complains of frequent defecation and liquid blood-streaked
stools with mucus admixtures, diffuse pain in the inferolateral abdomen, 6 kg weight loss over
the previous month. Objectively: body temperature - 37, 4oC, malnutrition, skin is pale and dry.
Abdomen is soft, sigmoid is painful and spasmodic, makes a rumbling sound. Liver is dense,
painful, extends 3 cm below the costal margin. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Non-specific ulcerative colitis
B. Bacillary dysentery
C. Sprue
D. Intestinal enzymopathy
E. Helminthic invasion
Explanation: Nonspecific ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the colon and rectum , which develops starting from the rectum. Usually, the periods of exacerbation of ulcerative colitis alternate with the absence of its evident symptoms.
83). A 50-year-old patient complains about having pain attacks in the right subcostal area for
about a year. He pain arises mainly after taking fattening food. Over the last week the attacks
occurred daily and became more painful. On the 3rd day of hospitalization the patient
presented with icteritiousness of skin and scleras, lightcolored feces and dark urine. In blood:
neutrophilic leukocytosis - 13, 1 · 109/l, ESR- 28 mm/h. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Chronic calculous cholecystitis
B. Chronic recurrent pancreatitis
C. Fatty degeneration of liver
D. Chronic cholangitis, exacerbation stage
E. Hypertensive dyskinesia of gallbladder
Explanation: lightcolored feces and dark urine indicate obstructive jaundice(icteritiousness of skin and scleras). Increase ESR and leucocytosis indicate inflammation. Right subcostal pain for one year it means chronic.
84). A 6-year-old child has duodenal ulcer. What antibacterial drug should be coadministered
together with metronidazole and De-Nol in order to eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection?
A. Amoxicillin
B. Tetracycline
C. Oleandomycin
D. Biseptol
E. Sulfadimethoxinum
Explanation: Triple therapy = PPI, Amoxycillin, clarithromysin.
Quadraple therapy: Bismuth(De-nol), ppI, metronidazole, tetracycline.
Note: Amoxicillin is given with metronidazole and denol along with PPI.
85). A 35-year-old patient complains of heartburn, sour eructation, burning, compressing
retrosternal pain and pain along the esophagus rising during forward bending of body. The
patient hasn’t been examined, takes Almagel on his own initiative, claims to feel better after its
taking. Make a provisional diagnosis:
A. Gastroesophageal reflux disease
B. Functional dyspepsia
C. Cardiospasm
D. Gastric ulcer
E. Duodenal ulcer
Explanation: Main feature of Gastroesophageal reflux is substernal pain during swallowing which is aggravated during bending forward. Heartburn due to acid reflux.
86). A patient complains of retrosternal pain, difficult swallowing, over 10 kg weight loss within
three months, general weakness. In blood: hypochromic anaemia, neutrophilic leukocytosis. In
feces: weakly positive Gregersen’s reaction. On esophagram a filling defect with ill-defined
serrated edges shows up along a large portion of the esophagus. What is the most likely
diagnosis?
A. Esophageal carcinoma
B. Benign tumour
C. Esophageal achalasia
D. Peptic ulcer
E. Sideropenic dysphagia
Explanation: sudden weight loss is alarm sign of cancer and patient have difficult in swallowing, esophagram show ill defined edge indicate esophageal cancer.
87).A 13-year-old girl has a 5-year history of pain in the right hypochondrium irradiating to the right
shoulder blade. The pain attacks are usually associated with diet violations, they are short and can be
easily relieved by antispasmodic drugs. During a pain attack, palpation of the abdomen is painful, the
pain is most intensive in the projection of the gallbladder. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Biliary dyskinesia
B.Chronic cholecystitis
C.Chronic gastroduodenitis
D.Chronic pancreatitis
E.Duodenal ulcer
Explanation: Biliary dyskinesia is a motility disorder that affects the gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi. The motility disorder of the gallbladder is called gallbladder dyskinesia. antispasmodic drug relief the pain.
88).A 48-year-old male patient complains of constant pain in the upper abdomen, mostly on the left, that is getting worse after taking meals; diarrhea, weight loss. The patient is an alcohol abuser. 2 years ago he had acute pancreatitis. Blood amylase is 4 g/h·l. Coprogram shows steatorrhea, creatorrhea. Blood glucose is 6,0 mmol/l. What treatment is indicated forth is patient?
A.Panzinorm forte
B.Insulin
C.Gastrozepin
D.Contrycal
E.No-spa
Explanation :This patient suspect to have chronic pancreatitis because history of acute pancreatitis and coprogram show steatorrhea so pancreatic enzyme(panzinorm forte) should be replaced.
89).A 24-year-old female patient complains of pain in the right hypochondrium that is getting worse after taking meals; nausea, fever up to37,7oC, icteric skin, pain in the large joints. These presentations have been observed for 8 months. Objectively: hepatosplenomegaly. Blood test results: ESR- 47 mm/h, total bilirubin - 86,1 mmol/l, direct bilirubin - 42,3 mmol/l. Total protein - 62 g/l, albumins - 40%, globulins - 60%, gamma globulins - 38%. Viral hepatitis markers were not detected. The antibodies to smooth muscle cells are present. On ultrasound the portal vein diameter was of 1 cm. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Autoimmune hepatitis
B.Primary biliary cirrhosis
C.Gilbert’s syndrome
D.Cholangiogenic hepatitis
E.Hemachromatosis
Explanation: Antibodies to smooth muscle cells specific for Autoimmune hepatitis.
90). A 57-year-old female complains of having a sensation of esophageal compresion, palpitation, difficult breathing during eating solid food, occasional vomiting with a full mouth, "wet pillow"sign at night for the last 6 months. Objectively: body tempearture -39 oC, height - 168 cm, weight - 72 kg, Ps- 76/min, АP- 120/80 mm Hg. X-ray revealed a considerable dilation of esophagus and its constriction in the cardial part. What pathology is most likely to have caused dysphagia in this patient?
A.Achalasia cardiae
B.Primary esophagism
C.Hiatal hernia
D.Esophageal carcinoma
E.Reflux esophagitis
Explanation: Achalasia is a condition in which the muscles of the lower part of the oesophagus fail to relax, preventing solid and liquid food from passing into the stomach. Bird beak or rat tail (esophageal dilatation with level of fluid ) radiological sign is specific for achalasia.
91). A 64-year-old patient has been referred to planned hospitalization for general weakness, poor appetite, progressive jaundice which appeared over 3 weeks ago and wasn’t accompanied by pain syndrome. Objectively: body temperature is at the rate of 36,8oC,Ps-78/min, abdomen is soft and painless, the symptoms of peritoneal irritation are present, palpation reveals a dramatically enlarged, tense gallbladder. What disease are these symptoms typical for?
A.Cancer of the pancreatic head
B.Duodenal ulcer
C.Acute cholecystitis
D.Chronic cholecystitis
E.Lamblia-induced cholecystitis
Explanation: Elderly is risk factor. weight is alarm sign for cancer. enlarged, tense gallbladder due to bile outflow obstruction by pancreatic head cancer.
92).A patient is 31 years old. Double-contrast barium swallow revealed a filling defect on the posterior wall in the middle segment of esophagus. The defect looked like a well-defined oval 1,8x1,3 cm large. Mucosal folds adjacent to the defect were intact, peristalsis and elasticity of the walls remained unchanged. Digestive tract problems were absent. What is the provisional diagnosis?
A.Esophageal tumour
B.Achalasia cardia
C.Esophageal burn
D.Diverticulum
E.Barrett’s esophagus
Explanation :- Double-contrast barium swallow revealed a filling defect on the posterior wall in the middle segment of esophagus and well defined oval mass indicate esophageal tumor.
93). A 28-year-oldmale patient complains of regurgitation, cough and heartburn that occurs every day after a meal, when bending forward or lying down. These problems have been observed for 4 years. Objective status and laboratory values are normal. FEGDS revealed endoesophagitis. What is leading
factor in the development of this disease?
A.Failure of the inferior esophageal sphincter
B.Hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid
C.Duodeno-gastric reflux
D.Hypergastrinemia
E.Helicobacter pylori infection
Explanation: patient had specific character of GERD(Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive disease. GERD occurs when stomach acid or, occasionally, stomach content, flows back into food pipe (esophagus) and reflux irritates the lining of esophagus and causes GERD)
94).A 33-year-old female complains of escalating spastic pain in the abdomen after the psycho-emotional stress. The patient has intermittent bowel movements, that is 2-3 bowel movements after waking up alternate with constipation lasting for 1-2 days. Objectively: body weight is unchanged, there is moderate pain on palpation of the sigmoid colon. Hb- 130 g/l, WBC-5,2· 109/l, ESR- 9mm/h. Proctosigmoidoscopy causes pain due to spastic bowel condition, intestinal mucosa is not changed. In the lumen there is a lot of mucus. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A.Irritable bowel syndrome
B.Crohn’s disease
C.Non-specific ulcerative colitis
D.Acute bowel ischemia
E.Malabsorption syndrome
Explanation : Diagnostic Criteria for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) :
1) Recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort at least 3 days/month in the last 3 months
Plus two or more of the following
2) Improvement with defecation
3) change in frequency of stool
4) change in stool form(appearance)
Note: There is no pathological changes in bowel.
95.A 44-year-old male patient complains of severe non-localized abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder girdle, repeated vomiting, red urine. The onset of the disease is associated with alcohol consumption. The face is hyperemic. AP- 70/40 mm Hg. Abdominal radiography reveals no pathological shadows. Hemodiastase is 54 mg/h/l. Prothrombin is 46%. What is the provisional diagnosis?
A.Acute pancreatitis
B.Acute myocardial infarction
C.Perforated gastric ulcer
D.Thrombosis of mesenteric vessels
E.Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta
Explanation: Acute pancreatitis is associated with alcohol consumption.
96).A 40-year-old male patient has had heaviness in the epigastric region for the last 6 months. He has not undergone any examinations. The night before, he abused vodka. In the morning there was vomiting, and 30 minutes after physical activity the patient experienced dizziness and profuse hematemesis. What pathology should be suspected in the first place?
A.Mallory-Weis’s syndrome
B.Menetrier’s disease
C.Gastric ulcer
D.Perforated ulcer
E.Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Explanation: Mallory-Weiss syndrome (MWS) is a condition marked by a tear in the mucous membrane, or inner lining, where the esophagus meets the stomach. It is mainly caused by severe repeated vomiting and alcoholism.
97).A 46-year-old male patient complains of periodic epigastric pain that occurs at night. Objectively: HR- 70/min, AP- 125/75 mm Hg, tenderness in the epigastric region is present. EGD confirms duodenal ulcer of 0,6 cm in diameter. Test for H. Pylori is positive. Which of the given antisecretory drugs will be a compulsory element of the treatment regimen?
A.Omeprazole
B.Famotidine
C.Pirenzepine
D.Atropine
E.Maalox
Explanation: Triple therapy = PPI(omeprazole), Amoxycillin, clarithromysin.
Quadraple therapy: Bismuth(De-nol), ppI, metronidazole, tetracycline.
98).A 49-year-old male patient complains of retrosternal pain, heartburn, weight loss of 8kg over the last year, constipation, weakness. The patient has been a smoker for 20 years, and has a 10-year history of Gastroesophageal reflux disease. The patient is asthenic, has dry skin. EGD revealed an ulcer in the lower third of the esophagus and esophageal stricture accompanied by edema, hyperemia and multiple erosions of the mucosa. What study is required for more accurate diagnosis?
A.Biopsy of the esophageal mucosa
B.X-ray examination of the esophagus
C.Respiratory test for Helicobacter pylori
D.pH-metry of the esophagus and the stomach
E.Fecal occult blood test
Explanation :- Above mentioned is elderly, smoker patient and have the history of GERD and there is loss of weight which is alarm sign for cancer. thus patient is suspected to have esophageal cancer because of esophageal erosion, stricture, edema. The best method of investigation in this case is Biopsy of the esophageal mucosa.

Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, please let me know