Correct answer for all Question is A
26). A 42 y.o. man who has been ill with duodenal ulcer for 20 years complains of getting a
sense of heaviness in stomach after meal, foul-smelling eructation, vomiting, weight loss.
Objectively: his state is relatively satisfactory, tissue turgor is diminished. On palpation the belly
is soft, there are no symptoms of peritenium irritation, "splashing sounds"in epigastrium.
Defecation - once in 3 days. What complication corresponds with the patient’s state and
described clinical presentations?
A. Ulcerative pyloric stenosis
B. Concealed ulcer perforation
C. Stomach cancer
D. Ulcer penetration
E. Chronic pancreatitis
Explanation: Duodenal ulcer is one of rick factor for pyloric stenosis. Heaviness in stomach after meal, foul-smelling eructation, weight loss due to pyloric stenosis.
27). A 63 y.o. woman complains of motiveless weakness, rapid fatigability, loss of appetite,
aversion to meat. Two days ago she had stomach bleeding. Objectively: temperature - 37, 50,
BR- 20/min, Ps- 96/min, AP- 110/75 mm Hg. On palpation in epigastrium - pain and muscle
tension. Blood count: Hb- 82 g/L, ESR- 35 mm/h. What examination will allow to make a
diagnosis?
A. Cytologic
B. Radiography
C. Endoscopy
D. Stomach content examination
E. Coprology
Explanation: Cytology is that branch of life science that deals with the study of cells in terms of structure, function and chemistry.Above patient is elderly( 63 yr) has alarm sign stomach bleeding , ESR ( 35 mm/h) elevated ,motiveless weakens ,rapid fatigability ,loss of appetite aversion to meat suspect to have cancer . Thus, cytologic study is done in order to confirm cancer.
28). A 41 y.o. woman has suffered from nonspecific ulcerative colitis for 5 years. On
rectoromanoscopy: evident inflammatory process of lower intestinal parts, pseudopolyposive
changes of mucous membrane. In blood: WBC- 9, 8∗109/L, RBC- 3, 0∗1012/L, sedimentation
rate - 52 mm/hour. What medication provides pathogenetic treatment of this patient?
A. Sulfasalasine
B. Motilium
C. Vikasolum
D. Linex
E. Kreon
Explanation: Drug of choice for Ulcerative colitis is sulfasalizine.
29). Plan radiography of the patient’s abdominal cavity reveals some hemispherical lucent
areas situated above distinct horizontal levels. What is the cause of such X-ray picture?
A. Intestinal obstruction
B. Perforative ulcer
C. Meteorism
D. Cancer of large intestine
E. Price’s disease
Explanation: Hemispherical lucent area situated above distinct horizontal levels is xray sign of intestinal obstruction.
30). An 8 y.o. boy was ill with B hepatitis one year ago. In the last 2 months he has complaints
of undue fatiguability, sleep disorder, appetite loss, nausea, especially in the mornings. Skin isn’t icterious, liver and spleen are 1 cm below the costal margins, painless. Alanineaminotransferase activity is 2,2 mcmolL. How can this condition be estimated?
A. Development of chronic hepatitis
B. Recurrance of viral hepatitis type B
C. Biliary dyskinesia
D. Residual effects of old viral hepatitis type B
E. Development of liver cirrhosis
Explanation: History of hepatitis B one year ago.
31). A patient is 65 y.o. He has been a smoker for 40 years. Hew has lost 10 kg during the last 3
months. Complains of pain in the epigastric area after taking meals, diarrhea, jaundice. Physical
examination revealed enlarged, painless gallbladder. Feces are light-coloured and clay-like.
Blood analysis revealed increased level of whole and direct bilirubin, alkaline phosphotase and
glutaminepyruvate transferase. Clinical urine analysis showed positive bilirubin reaction and
negative urobilinogene reaction. Where is the initial process that caused these changes?
A. In pancreas
B. In common bile duct
C. In liver
D. In duodenum
E. In gallbladder
Explanation: Feces is light color it means patient has obstructive jaundice that is caused by cancer developed on pancreatic head. Gallbladder enlarged due to bile flow obstruction by pancreatic head cancer. Elderly, smoking is risk factor. weight is alarm sign for cancer.
32). A 75 y.o. man has acute pain in the paraumbilical region accompanied by vomiting and
feeling of abdominal swelling in approximately 30 minutes after meals. He lost 10 kg during the
last months because he doesn’t eat in order to avoid pain. Abdomen examination reveals no
changes in the periods between pain attacks. Above the right femoral artery a murmur can be
auscultated, peripheral pulsation in the lower extrimities is weak. X-ray examination of stomach
and colonoscopy reealed no changes. What is the leading factor of this pathogenesis?
A. Ischemia
B. Psychogenic changes
C. Neoplastic process
D. Inflammation
E. Transient obstruction
Explanation :Elderly patients most viable to develop atherosclerosis and it causes blockade of artery resulting ischemia. in above situation,murmur was due to blockade of right femoral artery,and weak peripheral pulse.
33). A 38 y.o. woman was hospitalized to the surgical unit with acute abdominal pain irradiating
to the spine and vomiting. On laparocentesis hemmorhagic fluid is obtained. What disease is
suspected?
A. Acute pancreatitis
B. Renal colic
C. Acute enterocolitis
D. Perforative gastric ulcer
E. Acute appendicitis
Explanation : Acute abdominal pain irradiating to the spine is hallmark for pancreatitis. pancreas location retroperitoneal. Acute pancreatitis is associated with alcoholism. Diagnosis- hemorrhagic pancreatitis.
34). A 28 y.o. man fell seriously ill, he feels chill, has got a fever, body temperature raised up to
38, 50, paroxysmal pain in the left iliac region, frequent defecation in form of fluid bloody and
mucous mass. Abdomen palpation reveals painfulness in its left half, sigmoid colon is spasmed.
What is the most probable diagnosis?
A. Acute dysentery
B. Amebiasis
C. Colibacillosis
D. Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
E. Malignant tumors of large intestine
Explanation:Dysentery is an intestinal inflammation, especially in the colon, that can lead to severe diarrhea with mucus or blood in the feces. Patients typically experience mild to severe abdominal pain or stomach cramps.
35). A 50 y.o. woman for 1 year complained of attacks of right subcostal pain after fatty meal.
Last week the attacks have repeated every day and become more painful. What diagnostic
study would you recommend?
A. Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder
B. Liver function tests
C. X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract
D. Ultrasound study of the pancreas
E. Blood cell count
Explanation: patient suspected to have cholecystitis so gold standard is USG of gallbladder .
36). A 39 y.o. woman complaines of squeezed epigastric pain 1 hour after meal and heartburn.
She had been ill for 2 years. On palpation, there was moderate tenderness in pyloroduodenal
area. Antral gastritis was revealed on gastroscopy. What study can establish genesis of the
disease?
A. Revealing of Helicobacter infection in gastric mucosa
B. Detection of autoantibodies in the serum
C. Gastrin level in blood
D. Examination of stomach secretion
E. Examination of stomach motor function
Explanation: Helicobacter is most prevalence in antrum area and leads to antral gastritis.
37). A patient complains of feeling heaviness behind his breast bone, periodical sensation of
food stoppage, dysphagy. During the X-ray examination barium contrast revealed a single
saccular outpouching of anterodextral esophagus wall with regular contours and rigidly
outlined neck. What is the most probable diagnosis?
A. Esophageal diverticulum
B. Cancer of esophagus
C. Hiatal hernia
D. Varix dilatation of esophageal veins
E. Esophageal polyp
Explanation:X-ray barium contrast revealed a single saccular outpouching of anterodextral esophagus wall which indicates esophageal diverticulum.
38). A patient suffers from chronic recurrent pancreatitis with evident disturbance of
exocrinous function. After intake of rich spicy food and spirits his stool becomes fatty. Reduced
production of what factor is the most probable cause of steatorrhea?
A. Lipase
B. Tripsin
C. Acidity of gastric juice
D. Amylase
E. Alkaline phosphatase
Explanation: Pancreatic enzyme (lipase) which is essential for conversion of triglyceride to monoglycerides and free fatty acids which is absorbed. Due to lipase deficiency cause fatty stool. Thus, chronic pancreatitis is treated by pancreatic enzyme replacement (pancreatine).
39). A 45 y.o. man complains of having intensive pain in the epigastric region 1,5- 2 hours later
after food intake. He has been suffering from ulcer for 11 years. Objectively: t 0- 36, 50, RR-
16/min, Ps- 70 bpm, AP- 120/80 mm Hg. On palpation: local painfulness in the right epigastric
region. What parameters of intragastric Ph-meter in the region of stomach body are the most
typical for this patient’s disease?
A. рН = 1,0-2,0
B. рН = 3,0-4,0
C. рН = 4,0-5,0
D. рН = 5,0-6,0
E. рН = 6,0-7,0
Explanation:As Ph( 1,0-2,0) value decrease means more acidity and intensive pain indicate high acidity.
40). A patient with hepatic cirrhosis drank some spirits that resulted in headache, vomiting,
aversion to food, insomnia, jaundice, fetor hepaticus, abdominal swelling. What complication of
hepatic cirrhosis is meant?
A. Hepatocellular insufficiency
B. Hemorrhage from varicosely dilatated veins of esophagus
C. Portal hypertension
D. Acute stomach ulcer
E. Thrombosis of mesenteric vessels
Explanation: Hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology.
Fetor hepaticus also known as breath of the dead or hepatic foetor, is a condition seen in portal hypertension where portosystemic shunting allows thiols(sulfur containing analogue of alcohols) to pass directly into the lungs.
In this patient have headache, insomnia due to accumulation of nitrogenous compound.
41). A 48 year old man complains of fatique and shortness of breath. His Ht is 32%, and Hb - 103
g/l. Peripheral blood smear reveals macrocytosis. Serum vitamin B12 level is 90 pg/ml (normal
is 170 to 940); serum folate level is 6 ng/ml (normal is 2 to 14). Possible causes to consider
include all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Colonic diverticulitis
B. Vegetarianism
C. Regional enteritis
D. Pancreatitis
E. Fish tapeworm infection
Explanation: Cause of vitamin B12 deficiency include: Vegetarianism (low dietary content), Regional enteritis ( B12 readily absorbed in the last part of the small intestine i.e ileum) Pancreatitis (Vitamin B12 bind two carrier proteins haptocorrin [R binder] and intrinsic factor, but only its binding to intrinsic factor allows its absorption and R binder is removed by pancreatic enzyme which is defficient in pancreatitis), Fish tapeworm infection (parasite absorbing 80% or more of the host's B12 intake)
42). A 41 year old patient was admitted to the intensive care unit with haemorrhagic shock due
to gastric bleeding. He has a history of hepatitis B during the last 5 years. The source of
bleeding are esophageal veins. What is the most effective method for control of the bleeding?
A. Introduction of obturator nasogastric tube
B. Intravenous administration of pituitrin
C. Hemostatic therapy
D. Operation
E. Administration of plasma
Explanation: Esophageal Veins begin to dilate and swell as a result of increased blow flow. Cirrhosis is the most common cause of portal hypertension which lead to esophageal bleeding The goal of treatment is to stop acute bleeding as soon as possible by blakemore obturator tube.
43). A 75 year old man who has been suffering from diabetes for the last six months was found
to be jaundiced. He was asymptomatic except for weight loss at the rate of 10 pounds in 6
months. Physical examination revealed a hard, globular, right upper quadrant mass that moves
during respiration. A CT scan shows enlargement of the head of the pancreas, with no filling
defects in the liver. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Carcinoma of the head of the pancreas
B. Infectious hepatitis
C. Haemolytic jaundice
D. Malignant biliary stricture
E. Metastatic disease of liver
Explanation: Elderly is risk factor. weight is alarm sign for cancer. On examination, hard, globular mass which move during respiration . CT scan shows enlargement of the head of the pancreas that indicate cancer.
44). A 50 year old woman complained of attacks of right subcostal pain after fatty meal she has
been suffering from for a year. Last week the attacks repeated every day and became more
painful. What diagnostic study would you recommend?
A. Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder
B. Liver function tests
C. X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract
D. Ultrasound study of the pancreas
E. Blood cell count
Explanation: patient suspected to have cholecystitis so gold standard is USG of gallbladder .
45). During an operation for presumed appendicitis the appendix was found to be normal;
however, the terminal ileum is evidently thickened and feels rubbery, its serosa is covered with
grayish-white exudate, and several loops of apparently normal small intestine are adherent to
it. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Crohn’s disease of the terminal ileum
B. Perforated Meckel’s diverticulum
C. Ulcerative colitis
D. Ileocecal tuberculosis
E. Acute ileitis
Explanation:Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus.Mostly affected in crohn's disease is terminal ileum. Skip lesion, transmural involvement are main characteristic of this disease.
46). A 68 year old patient has been suffering from chronic pancreatitis for 35 years. During the
last 5 years he has been observing abatement of pain syndrome, abdominal swelling, frequent
defecations up to 3-4 times a day (feces are greyish, glossy, with admixtures of undigested
food), progressing weight loss. Change of symptom set is caused by joining of:
A. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
B. Endocrine pancreatic insufficiency
C. Syndrome of lactase deficiency
D. Irritable bowels syndrome
E. Chronic enterocolitis
Explanation: Main function of exocrine part of pancreas is production of enzyme i.e pancreatic amylase, lipase, proteases. Chronic pancreatitis lead to these enzyme deficiency resulting in undigestion(undigested food in stool).
47). A 32 year old patient complains about heartburn and dull pain in the epigastrium that
appear 2-3 hours after meal. Exacerbations happen in spring and in autumn. The patient has
food intolerance of eggs and fish. Objectively: stomach palpation reveals painfulness in the
gastroduodenal area. Electrophasoduodenoscopy revealed a 5 mm ulcer on the anterior wall of
duodenum. Urease test is positive. What is the most probable leading mechanism of disease
development?
A. Helicobacterial infection
B. Dietary allergy
C. Autoantibody production
D. Reduced prostaglandin synthesis
E. Disorder of gastric motor activity
Explanation:- Urease test positive reaveles Helicobacterial infection.
48). A 10 year old girl complains about abdominal pain that is arising and getting worse after
eating rough or spicy food. She complains also about sour eructation, heartburn, frequent
constipations, headache, irritability. She has been suffering from this for 12 months.
Objectively: the girl’s diet is adequate. Tongue is moist with white deposit at the root.
Abdomen is soft, painful in its epigastric part. What study method will help to make a
diagnosis?
A. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
B. Intragastral pH-metry
C. Fractional examination of gastric juice
D. Contrast roentgenoscopy
E. Biochemical blood analysis
Explanation: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is gold standard for GERD.
49). A patient complains about pyrosis and permanent pain behind his breastbone. When he
bends forward after eating there appears regurgitation. Roentgenological examination revealed
extrasaccular cardiofunctional hernia of esophageal opening of diaphragm. Esophagoscopy
revealed signs of reflux-esophagitis. What is the necessary tretment tactics?
A. Operation in a surgical department
B. Conservative treatment in an outpatients’ clinic
C. Conservative treatment in the therapeutic hospital
D. Conservative treatment in a surgical department
E. Treatment at a health resort
Explanation:-hernia of esophageal opening of diaphragm is emergency case so patient should be operated as soon as possible.
50). A 12 year old child has the ulcer disease of stomach. What is the etiology of this disease?
A. Intestinal bacillus
B. Helicobacter pylory
C. Salmonella
D. Lambliosis
E. Influenza
Explanation:ulcer disease is mainly caused by H. pylory but in krok base answer given Intestinal bacillus.
To be continued.. part 3
26). A 42 y.o. man who has been ill with duodenal ulcer for 20 years complains of getting a
sense of heaviness in stomach after meal, foul-smelling eructation, vomiting, weight loss.
Objectively: his state is relatively satisfactory, tissue turgor is diminished. On palpation the belly
is soft, there are no symptoms of peritenium irritation, "splashing sounds"in epigastrium.
Defecation - once in 3 days. What complication corresponds with the patient’s state and
described clinical presentations?
A. Ulcerative pyloric stenosis
B. Concealed ulcer perforation
C. Stomach cancer
D. Ulcer penetration
E. Chronic pancreatitis
Explanation: Duodenal ulcer is one of rick factor for pyloric stenosis. Heaviness in stomach after meal, foul-smelling eructation, weight loss due to pyloric stenosis.
27). A 63 y.o. woman complains of motiveless weakness, rapid fatigability, loss of appetite,
aversion to meat. Two days ago she had stomach bleeding. Objectively: temperature - 37, 50,
BR- 20/min, Ps- 96/min, AP- 110/75 mm Hg. On palpation in epigastrium - pain and muscle
tension. Blood count: Hb- 82 g/L, ESR- 35 mm/h. What examination will allow to make a
diagnosis?
A. Cytologic
B. Radiography
C. Endoscopy
D. Stomach content examination
E. Coprology
Explanation: Cytology is that branch of life science that deals with the study of cells in terms of structure, function and chemistry.Above patient is elderly( 63 yr) has alarm sign stomach bleeding , ESR ( 35 mm/h) elevated ,motiveless weakens ,rapid fatigability ,loss of appetite aversion to meat suspect to have cancer . Thus, cytologic study is done in order to confirm cancer.
28). A 41 y.o. woman has suffered from nonspecific ulcerative colitis for 5 years. On
rectoromanoscopy: evident inflammatory process of lower intestinal parts, pseudopolyposive
changes of mucous membrane. In blood: WBC- 9, 8∗109/L, RBC- 3, 0∗1012/L, sedimentation
rate - 52 mm/hour. What medication provides pathogenetic treatment of this patient?
A. Sulfasalasine
B. Motilium
C. Vikasolum
D. Linex
E. Kreon
Explanation: Drug of choice for Ulcerative colitis is sulfasalizine.
29). Plan radiography of the patient’s abdominal cavity reveals some hemispherical lucent
areas situated above distinct horizontal levels. What is the cause of such X-ray picture?
A. Intestinal obstruction
B. Perforative ulcer
C. Meteorism
D. Cancer of large intestine
E. Price’s disease
Explanation: Hemispherical lucent area situated above distinct horizontal levels is xray sign of intestinal obstruction.
30). An 8 y.o. boy was ill with B hepatitis one year ago. In the last 2 months he has complaints
of undue fatiguability, sleep disorder, appetite loss, nausea, especially in the mornings. Skin isn’t icterious, liver and spleen are 1 cm below the costal margins, painless. Alanineaminotransferase activity is 2,2 mcmolL. How can this condition be estimated?
A. Development of chronic hepatitis
B. Recurrance of viral hepatitis type B
C. Biliary dyskinesia
D. Residual effects of old viral hepatitis type B
E. Development of liver cirrhosis
Explanation: History of hepatitis B one year ago.
31). A patient is 65 y.o. He has been a smoker for 40 years. Hew has lost 10 kg during the last 3
months. Complains of pain in the epigastric area after taking meals, diarrhea, jaundice. Physical
examination revealed enlarged, painless gallbladder. Feces are light-coloured and clay-like.
Blood analysis revealed increased level of whole and direct bilirubin, alkaline phosphotase and
glutaminepyruvate transferase. Clinical urine analysis showed positive bilirubin reaction and
negative urobilinogene reaction. Where is the initial process that caused these changes?
A. In pancreas
B. In common bile duct
C. In liver
D. In duodenum
E. In gallbladder
Explanation: Feces is light color it means patient has obstructive jaundice that is caused by cancer developed on pancreatic head. Gallbladder enlarged due to bile flow obstruction by pancreatic head cancer. Elderly, smoking is risk factor. weight is alarm sign for cancer.
32). A 75 y.o. man has acute pain in the paraumbilical region accompanied by vomiting and
feeling of abdominal swelling in approximately 30 minutes after meals. He lost 10 kg during the
last months because he doesn’t eat in order to avoid pain. Abdomen examination reveals no
changes in the periods between pain attacks. Above the right femoral artery a murmur can be
auscultated, peripheral pulsation in the lower extrimities is weak. X-ray examination of stomach
and colonoscopy reealed no changes. What is the leading factor of this pathogenesis?
A. Ischemia
B. Psychogenic changes
C. Neoplastic process
D. Inflammation
E. Transient obstruction
Explanation :Elderly patients most viable to develop atherosclerosis and it causes blockade of artery resulting ischemia. in above situation,murmur was due to blockade of right femoral artery,and weak peripheral pulse.
33). A 38 y.o. woman was hospitalized to the surgical unit with acute abdominal pain irradiating
to the spine and vomiting. On laparocentesis hemmorhagic fluid is obtained. What disease is
suspected?
A. Acute pancreatitis
B. Renal colic
C. Acute enterocolitis
D. Perforative gastric ulcer
E. Acute appendicitis
Explanation : Acute abdominal pain irradiating to the spine is hallmark for pancreatitis. pancreas location retroperitoneal. Acute pancreatitis is associated with alcoholism. Diagnosis- hemorrhagic pancreatitis.
34). A 28 y.o. man fell seriously ill, he feels chill, has got a fever, body temperature raised up to
38, 50, paroxysmal pain in the left iliac region, frequent defecation in form of fluid bloody and
mucous mass. Abdomen palpation reveals painfulness in its left half, sigmoid colon is spasmed.
What is the most probable diagnosis?
A. Acute dysentery
B. Amebiasis
C. Colibacillosis
D. Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
E. Malignant tumors of large intestine
Explanation:Dysentery is an intestinal inflammation, especially in the colon, that can lead to severe diarrhea with mucus or blood in the feces. Patients typically experience mild to severe abdominal pain or stomach cramps.
35). A 50 y.o. woman for 1 year complained of attacks of right subcostal pain after fatty meal.
Last week the attacks have repeated every day and become more painful. What diagnostic
study would you recommend?
A. Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder
B. Liver function tests
C. X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract
D. Ultrasound study of the pancreas
E. Blood cell count
Explanation: patient suspected to have cholecystitis so gold standard is USG of gallbladder .
36). A 39 y.o. woman complaines of squeezed epigastric pain 1 hour after meal and heartburn.
She had been ill for 2 years. On palpation, there was moderate tenderness in pyloroduodenal
area. Antral gastritis was revealed on gastroscopy. What study can establish genesis of the
disease?
A. Revealing of Helicobacter infection in gastric mucosa
B. Detection of autoantibodies in the serum
C. Gastrin level in blood
D. Examination of stomach secretion
E. Examination of stomach motor function
Explanation: Helicobacter is most prevalence in antrum area and leads to antral gastritis.
37). A patient complains of feeling heaviness behind his breast bone, periodical sensation of
food stoppage, dysphagy. During the X-ray examination barium contrast revealed a single
saccular outpouching of anterodextral esophagus wall with regular contours and rigidly
outlined neck. What is the most probable diagnosis?
A. Esophageal diverticulum
B. Cancer of esophagus
C. Hiatal hernia
D. Varix dilatation of esophageal veins
E. Esophageal polyp
Explanation:X-ray barium contrast revealed a single saccular outpouching of anterodextral esophagus wall which indicates esophageal diverticulum.
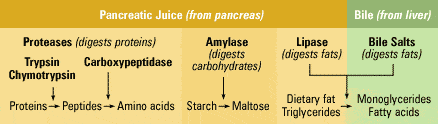
38). A patient suffers from chronic recurrent pancreatitis with evident disturbance of
exocrinous function. After intake of rich spicy food and spirits his stool becomes fatty. Reduced
production of what factor is the most probable cause of steatorrhea?
A. Lipase
B. Tripsin
C. Acidity of gastric juice
D. Amylase
E. Alkaline phosphatase
Explanation: Pancreatic enzyme (lipase) which is essential for conversion of triglyceride to monoglycerides and free fatty acids which is absorbed. Due to lipase deficiency cause fatty stool. Thus, chronic pancreatitis is treated by pancreatic enzyme replacement (pancreatine).
39). A 45 y.o. man complains of having intensive pain in the epigastric region 1,5- 2 hours later
after food intake. He has been suffering from ulcer for 11 years. Objectively: t 0- 36, 50, RR-
16/min, Ps- 70 bpm, AP- 120/80 mm Hg. On palpation: local painfulness in the right epigastric
region. What parameters of intragastric Ph-meter in the region of stomach body are the most
typical for this patient’s disease?
A. рН = 1,0-2,0
B. рН = 3,0-4,0
C. рН = 4,0-5,0
D. рН = 5,0-6,0
E. рН = 6,0-7,0
Explanation:As Ph( 1,0-2,0) value decrease means more acidity and intensive pain indicate high acidity.
40). A patient with hepatic cirrhosis drank some spirits that resulted in headache, vomiting,
aversion to food, insomnia, jaundice, fetor hepaticus, abdominal swelling. What complication of
hepatic cirrhosis is meant?
A. Hepatocellular insufficiency
B. Hemorrhage from varicosely dilatated veins of esophagus
C. Portal hypertension
D. Acute stomach ulcer
E. Thrombosis of mesenteric vessels
Explanation: Hepatic insufficiency is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology.
Fetor hepaticus also known as breath of the dead or hepatic foetor, is a condition seen in portal hypertension where portosystemic shunting allows thiols(sulfur containing analogue of alcohols) to pass directly into the lungs.
In this patient have headache, insomnia due to accumulation of nitrogenous compound.
41). A 48 year old man complains of fatique and shortness of breath. His Ht is 32%, and Hb - 103
g/l. Peripheral blood smear reveals macrocytosis. Serum vitamin B12 level is 90 pg/ml (normal
is 170 to 940); serum folate level is 6 ng/ml (normal is 2 to 14). Possible causes to consider
include all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Colonic diverticulitis
B. Vegetarianism
C. Regional enteritis
D. Pancreatitis
E. Fish tapeworm infection
Explanation: Cause of vitamin B12 deficiency include: Vegetarianism (low dietary content), Regional enteritis ( B12 readily absorbed in the last part of the small intestine i.e ileum) Pancreatitis (Vitamin B12 bind two carrier proteins haptocorrin [R binder] and intrinsic factor, but only its binding to intrinsic factor allows its absorption and R binder is removed by pancreatic enzyme which is defficient in pancreatitis), Fish tapeworm infection (parasite absorbing 80% or more of the host's B12 intake)
42). A 41 year old patient was admitted to the intensive care unit with haemorrhagic shock due
to gastric bleeding. He has a history of hepatitis B during the last 5 years. The source of
bleeding are esophageal veins. What is the most effective method for control of the bleeding?
A. Introduction of obturator nasogastric tube
B. Intravenous administration of pituitrin
C. Hemostatic therapy
D. Operation
E. Administration of plasma
Explanation: Esophageal Veins begin to dilate and swell as a result of increased blow flow. Cirrhosis is the most common cause of portal hypertension which lead to esophageal bleeding The goal of treatment is to stop acute bleeding as soon as possible by blakemore obturator tube.
43). A 75 year old man who has been suffering from diabetes for the last six months was found
to be jaundiced. He was asymptomatic except for weight loss at the rate of 10 pounds in 6
months. Physical examination revealed a hard, globular, right upper quadrant mass that moves
during respiration. A CT scan shows enlargement of the head of the pancreas, with no filling
defects in the liver. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Carcinoma of the head of the pancreas
B. Infectious hepatitis
C. Haemolytic jaundice
D. Malignant biliary stricture
E. Metastatic disease of liver
Explanation: Elderly is risk factor. weight is alarm sign for cancer. On examination, hard, globular mass which move during respiration . CT scan shows enlargement of the head of the pancreas that indicate cancer.
44). A 50 year old woman complained of attacks of right subcostal pain after fatty meal she has
been suffering from for a year. Last week the attacks repeated every day and became more
painful. What diagnostic study would you recommend?
A. Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder
B. Liver function tests
C. X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract
D. Ultrasound study of the pancreas
E. Blood cell count
Explanation: patient suspected to have cholecystitis so gold standard is USG of gallbladder .
however, the terminal ileum is evidently thickened and feels rubbery, its serosa is covered with
grayish-white exudate, and several loops of apparently normal small intestine are adherent to
it. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Crohn’s disease of the terminal ileum
B. Perforated Meckel’s diverticulum
C. Ulcerative colitis
D. Ileocecal tuberculosis
E. Acute ileitis
Explanation:Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus.Mostly affected in crohn's disease is terminal ileum. Skip lesion, transmural involvement are main characteristic of this disease.
46). A 68 year old patient has been suffering from chronic pancreatitis for 35 years. During the
last 5 years he has been observing abatement of pain syndrome, abdominal swelling, frequent
defecations up to 3-4 times a day (feces are greyish, glossy, with admixtures of undigested
food), progressing weight loss. Change of symptom set is caused by joining of:
A. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
B. Endocrine pancreatic insufficiency
C. Syndrome of lactase deficiency
D. Irritable bowels syndrome
E. Chronic enterocolitis
Explanation: Main function of exocrine part of pancreas is production of enzyme i.e pancreatic amylase, lipase, proteases. Chronic pancreatitis lead to these enzyme deficiency resulting in undigestion(undigested food in stool).
47). A 32 year old patient complains about heartburn and dull pain in the epigastrium that
appear 2-3 hours after meal. Exacerbations happen in spring and in autumn. The patient has
food intolerance of eggs and fish. Objectively: stomach palpation reveals painfulness in the
gastroduodenal area. Electrophasoduodenoscopy revealed a 5 mm ulcer on the anterior wall of
duodenum. Urease test is positive. What is the most probable leading mechanism of disease
development?
A. Helicobacterial infection
B. Dietary allergy
C. Autoantibody production
D. Reduced prostaglandin synthesis
E. Disorder of gastric motor activity
Explanation:- Urease test positive reaveles Helicobacterial infection.
48). A 10 year old girl complains about abdominal pain that is arising and getting worse after
eating rough or spicy food. She complains also about sour eructation, heartburn, frequent
constipations, headache, irritability. She has been suffering from this for 12 months.
Objectively: the girl’s diet is adequate. Tongue is moist with white deposit at the root.
Abdomen is soft, painful in its epigastric part. What study method will help to make a
diagnosis?
A. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
B. Intragastral pH-metry
C. Fractional examination of gastric juice
D. Contrast roentgenoscopy
E. Biochemical blood analysis
Explanation: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is gold standard for GERD.
49). A patient complains about pyrosis and permanent pain behind his breastbone. When he
bends forward after eating there appears regurgitation. Roentgenological examination revealed
extrasaccular cardiofunctional hernia of esophageal opening of diaphragm. Esophagoscopy
revealed signs of reflux-esophagitis. What is the necessary tretment tactics?
A. Operation in a surgical department
B. Conservative treatment in an outpatients’ clinic
C. Conservative treatment in the therapeutic hospital
D. Conservative treatment in a surgical department
E. Treatment at a health resort
Explanation:-hernia of esophageal opening of diaphragm is emergency case so patient should be operated as soon as possible.
50). A 12 year old child has the ulcer disease of stomach. What is the etiology of this disease?
A. Intestinal bacillus
B. Helicobacter pylory
C. Salmonella
D. Lambliosis
E. Influenza
Explanation:ulcer disease is mainly caused by H. pylory but in krok base answer given Intestinal bacillus.
To be continued.. part 3


Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, please let me know