Jaundice is yellowish discoloration of the skin, mucosa layers of mouth and sclera of eyes due to increase bilirubin in the blood serum.Jaundice is a symptom of a disease rather than a disease itself. the word jaundice came from French word "Jaune" thats means "yellow" . Jaundice in newborn babies is common condition. A newborn's babies may not have mature enough to clean out bilirubin. Fortunately,lots of cases of it in newborns go away on their own.
Scleral Icterus:- It's is a condition where there is yellowing of the whites of the eyes, mostly commonly seen in liver diseases patients.Yellow color of the eyes in scleral icterus patients can range from a muddying to a bright yellow or even an orange discoloration there is no any types of visual disturbances because of it.It is not a disease it self its a symptoms of a underling disease and it can resolve when the disease get treated in well manner.
Normal laboratory values:
Note: To have jaundice Total bilirubin should be more than 2-3 mg/dl or > 34 micro mol /l. If the ALP and GGT levels rise proportionately about as high as AST & ALT, it means cholestatic problems.If AST and ALT rise is significantly higher than ALP & GGT sise,it indicates as liver problems. Alcoholic liver damage shows AST 10 times higher than ALT. ALT highet than AST , indicate hepatitis ( viral). Bilirubin levels more than 10 to normal indicate neoplastic or intrahepatic cholestasis . AST levels greater than 15 times normal tends to indicate hepatocellular damage.less than this indicate obstructive cause. If ALP levels more than 5 times of normal indicate obstruction,where as levels more than 10 times normal indicate drug or toxic cholestatic hepatitis or cytomegalovirus (CMV). These two conditions can also have ALT & AST > 20 times normal. GGT > 10 times normal indicates cholestasis. Acetaminophen toxicity result in AST & ALT LEVELS > 50 times normal.
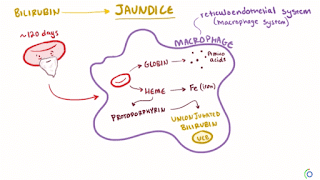
1.) Pre- hepatic /hemolytic jaundice :-
In this case pathology occurs prior to live . It's caused by hemolysis ( RBC breakdown) mainly due to certain genetic diseases eg. sickel cell anemia,thalassemia, G-6- phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, spherocytosis, etc. Increase break down RBCs leades to increase unconjugated ( indirect) bilirubin in blood and its deposition on various tissues of our body leads to jaundice appearance.Beside these hemolytic uremic syndrome may also play role . Gilbert's syndrom and result mild jaundice and Cigler -Najjar SYndrome ( Type 1 and II) also play role.
2.) Hepatocellular/hepatic jaundice :-
Pathology located within liver because of parenchymal cells of liver diseases.It's caused by acute or chronic hepatitis,hepatotoxicity ,cirrhosis, drug induced hepatitis ,alchol liver diseases,etc. Damaged cells reduces liver's capacity to metabolized and excrete bilirubin leading to build up of unconjugated (indirect) in the blood .
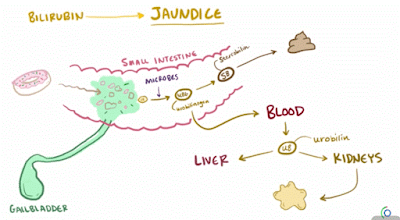
3.) Post -Hepatic /cholestatic jaundice :-
Pathology located after conjugation of unconjugated bilirubin with UGT ( Uridine Glucuronyl Transferase) enzyme as conjugated ( direct) bilirubin but not excrete well due to obstruction of biliary passage.Its also known as obstructive jaundice. following are most common causes - gallstones in common cystic duct, pancreatic head cancer, liver fluke may live in common bile duct and obstruct it, stricture of common bile duct, biliary atresia, cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatitis, cholestasis of pregnancy, pseudocysts of pancrease.
A.) Unconjugated ( fat soluble) :-
a.) Increase production of unconjugated bilirubin eg. prosthethic valve implantation ,etc.
b.) Decrease uptake :- due to certain drugs eg. cyclosporine,sulfonamides, rifampicin ,etc
c.) decrease conjugation ;- genetic disorders eg. Gilbert's syndrom and result mild jaundice and Cigler -Najjar SYndrome ( Type 1 and II).
B.) Conjugated ( water soluble) :- Dubin–Johnson syndrome (autosomal recessive) conjugated hyperbilirubinemia because of defective endogenous and exogenous transfer of anionic conjugates from hepatocytes into the bile. Impaired biliary excretion of bilirubin glucuronides is due to a mutation in the canalicular (MRP2). Darkly pigmented liver is due to polymerized epinephrine metabolites, not bilirubin. Rotor syndrome ( autosomal recessive).
2.) Liver Diseases: 2 types -
A.) Hepatocellular dysfunctions :-
I.) Acute - Due to hepatitis( viral, alcoholic ), drug induced , Hypertension (HTN) ischemic injury ,wilson's diseases etc.
II.) Chronic:- primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune conditions, hemochromatosis, fatty liver diseases, all chronic cause of hepatitis, Wilso's disease, etc.
.
B.) Predominent colesterol :- Syphilis,metastasis,etc.
3.) Post hepatic jaundice:-
Physical Examination:-
look for color of skin , sclera,oral mucus. Also look for palmar erythema, leukonychia, gynecomastia, spider nevi, caput nodosa, examine for ascities, hepatosplenomegaly. auscultate bowel sounds,etc.
Lab findings:-
CBC:- decrease hemoglobin, sign of anemia, may or may not present inflammatory markers.
Total bilirubin normal/increase, conjugated bilirubin normal, unconjugated bilirubin normal/increase, urobilinogen normal /increase, urine color normal, stool color normal, conjugated bilirubin in urine absent, AST, ALT, ALP normal, splenomegaly present.
Hepatic jaundice:-
Total bilirubin increase, conjugated bilirubin increase , unconjugated bilirubin increase, urobilinogen decrease, urine color dark, stool color normal/ pale, conjugated bilirubin in urine present, AST, ALT, ALP increase, splenomegaly present.
Post- hepatic jaundice:-
Total bilirubin increase , conjugated bilirubin increase , unconjugated bilirubin normal, urobilinogen decrease/negative, urine color dark, stool color pale, conjugated bilirubin in urine present, AST, ALT, ALP increase, splenomegaly present.
Note:- check level of albumin , prothrombin time, clotting factors , etc.
Other test if needed:- pancreatic enzyme test, kidney function test ,etc.
Instumental diagnosis approch:-
Life style modifications:- manage stress, regular exercise maintain hygenic wayof living, avoid iv drugs using, alcohol, smoking,etc.
Dite changes:-
less fatty food , fried and salty too, junk food, try to eat green leafy vegetables and fruits( papaya, apple, orange,etc), take enough leamon ,raddish , neem leaf , sugarcane juice etc.
Medical treatment:-
Treat underlying causes of liver diseases , symptomatic treatment , can use ursodeoxycholic acid in order to reduce itching. etc.
Surgical treatment:- splenectomy, cholecystectomy, surgical removal of gall stones , ichiness may help by draining the gallbladder etc.
Note:- New born baby may develop physiological jaundice first 2 days and then gradually resolve its own.Yellowish skin may occur but not jaundice in case of eating beta carotene rich food and medications like rifampin.
Scleral Icterus:- It's is a condition where there is yellowing of the whites of the eyes, mostly commonly seen in liver diseases patients.Yellow color of the eyes in scleral icterus patients can range from a muddying to a bright yellow or even an orange discoloration there is no any types of visual disturbances because of it.It is not a disease it self its a symptoms of a underling disease and it can resolve when the disease get treated in well manner.
Normal laboratory values:
- Alanine aminotransferase ( ALT):- 8-20 20 U/L
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST):- 8-20 U/L
- Bilirubin,serum (adult) Total // Direct:- 0.1- 1.2mg/dl,// < 0.3 mg/dl
- Indirect bilirubin:- 0.3- 1 mg/dl
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP):- female ( 30 -100 U/L or 0.5 - 1.67 mkat/L SI units), male ( 45-115 U/L or 0.75 -1.92 mkat/L SI units)
- Gamma- Glutamyl Transferase:- female (5-29 U/L), male (5-38 U/L),child (3-30 IU/l).

Note: To have jaundice Total bilirubin should be more than 2-3 mg/dl or > 34 micro mol /l. If the ALP and GGT levels rise proportionately about as high as AST & ALT, it means cholestatic problems.If AST and ALT rise is significantly higher than ALP & GGT sise,it indicates as liver problems. Alcoholic liver damage shows AST 10 times higher than ALT. ALT highet than AST , indicate hepatitis ( viral). Bilirubin levels more than 10 to normal indicate neoplastic or intrahepatic cholestasis . AST levels greater than 15 times normal tends to indicate hepatocellular damage.less than this indicate obstructive cause. If ALP levels more than 5 times of normal indicate obstruction,where as levels more than 10 times normal indicate drug or toxic cholestatic hepatitis or cytomegalovirus (CMV). These two conditions can also have ALT & AST > 20 times normal. GGT > 10 times normal indicates cholestasis. Acetaminophen toxicity result in AST & ALT LEVELS > 50 times normal.
Classification of jaundice on the basis of physiological mechanism the pathology effects
1.) Pre- hepatic /hemolytic jaundice :-
In this case pathology occurs prior to live . It's caused by hemolysis ( RBC breakdown) mainly due to certain genetic diseases eg. sickel cell anemia,thalassemia, G-6- phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, spherocytosis, etc. Increase break down RBCs leades to increase unconjugated ( indirect) bilirubin in blood and its deposition on various tissues of our body leads to jaundice appearance.Beside these hemolytic uremic syndrome may also play role . Gilbert's syndrom and result mild jaundice and Cigler -Najjar SYndrome ( Type 1 and II) also play role.
2.) Hepatocellular/hepatic jaundice :-
Pathology located within liver because of parenchymal cells of liver diseases.It's caused by acute or chronic hepatitis,hepatotoxicity ,cirrhosis, drug induced hepatitis ,alchol liver diseases,etc. Damaged cells reduces liver's capacity to metabolized and excrete bilirubin leading to build up of unconjugated (indirect) in the blood .
3.) Post -Hepatic /cholestatic jaundice :-
Pathology located after conjugation of unconjugated bilirubin with UGT ( Uridine Glucuronyl Transferase) enzyme as conjugated ( direct) bilirubin but not excrete well due to obstruction of biliary passage.Its also known as obstructive jaundice. following are most common causes - gallstones in common cystic duct, pancreatic head cancer, liver fluke may live in common bile duct and obstruct it, stricture of common bile duct, biliary atresia, cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatitis, cholestasis of pregnancy, pseudocysts of pancrease.
Other classification of jaundice / hyperbilirubinemia:-
1.) Isolated disorder of bilirubin metabolism :- It's 2 types as given below-A.) Unconjugated ( fat soluble) :-
a.) Increase production of unconjugated bilirubin eg. prosthethic valve implantation ,etc.
b.) Decrease uptake :- due to certain drugs eg. cyclosporine,sulfonamides, rifampicin ,etc
c.) decrease conjugation ;- genetic disorders eg. Gilbert's syndrom and result mild jaundice and Cigler -Najjar SYndrome ( Type 1 and II).
B.) Conjugated ( water soluble) :- Dubin–Johnson syndrome (autosomal recessive) conjugated hyperbilirubinemia because of defective endogenous and exogenous transfer of anionic conjugates from hepatocytes into the bile. Impaired biliary excretion of bilirubin glucuronides is due to a mutation in the canalicular (MRP2). Darkly pigmented liver is due to polymerized epinephrine metabolites, not bilirubin. Rotor syndrome ( autosomal recessive).
2.) Liver Diseases: 2 types -
A.) Hepatocellular dysfunctions :-
I.) Acute - Due to hepatitis( viral, alcoholic ), drug induced , Hypertension (HTN) ischemic injury ,wilson's diseases etc.
II.) Chronic:- primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune conditions, hemochromatosis, fatty liver diseases, all chronic cause of hepatitis, Wilso's disease, etc.
.
B.) Predominent colesterol :- Syphilis,metastasis,etc.

3.) Post hepatic jaundice:-
Signs and Symptoms:-
- pale-colored stools
- dark-colored urine
- skin itching / puritus
- nausea and vomiting
- rectal bleeding
- diarrhea
- fever and chills
- weakness/ lethargy
- weight loss
- loss of appetite
- confusion
- abdominal pain
- headache
- ascites
- yellowish color sclera ,skin ,oral mucosal
- caput medusa
- hepatosplenomegaly
- spider nevi
- palmar erythema ( chronic liver disease)
Diagnosis ( Investigations)
Patients History:- Ask patients about medications, travelling history ,family history of liver diseases, socioeconomic conditions , way of life living, IV drug user or not, diet habits ( specially fast foods, junk foods, fried food, etc), onset of diseases , skin itching, ask for constitutionals present or not, character of stool and urine,etc.Physical Examination:-
look for color of skin , sclera,oral mucus. Also look for palmar erythema, leukonychia, gynecomastia, spider nevi, caput nodosa, examine for ascities, hepatosplenomegaly. auscultate bowel sounds,etc.
Lab findings:-
CBC:- decrease hemoglobin, sign of anemia, may or may not present inflammatory markers.
Diagnostic approch for the patient with jaundice
Pre-hepatic jaundice:-Total bilirubin normal/increase, conjugated bilirubin normal, unconjugated bilirubin normal/increase, urobilinogen normal /increase, urine color normal, stool color normal, conjugated bilirubin in urine absent, AST, ALT, ALP normal, splenomegaly present.
Hepatic jaundice:-
Total bilirubin increase, conjugated bilirubin increase , unconjugated bilirubin increase, urobilinogen decrease, urine color dark, stool color normal/ pale, conjugated bilirubin in urine present, AST, ALT, ALP increase, splenomegaly present.
Post- hepatic jaundice:-
Total bilirubin increase , conjugated bilirubin increase , unconjugated bilirubin normal, urobilinogen decrease/negative, urine color dark, stool color pale, conjugated bilirubin in urine present, AST, ALT, ALP increase, splenomegaly present.
Liver Function Tests:-
To have jaundice Total bilirubin should be more than 2-3 mg/dl or > 34 micro mol /l. If the ALP and GGT levels rise proportionately about as high as AST & ALT, it means cholestatic problems.If AST and ALT rise is significantly higher than ALP & GGT sise,it indicates as liver problems. Alcoholic liver damage shows AST 10 times higher than ALT. ALT highet than AST , indicate hepatitis ( viral). Bilirubin levels more than 10 to normal indicate neoplastic or intrahepatic cholestasis . AST levels greater than 15 times normal tends to indicate hepatocellular damage.less than this indicate obstructive cause. If ALP levels more than 5 times of normal indicate obstruction,where as levels more than 10 times normal indicate drug or toxic cholestatic hepatitis or cytomegalovirus (CMV). These two conditions can also have ALT & AST > 20 times normal. GGT > 10 times normal indicates cholestasis. Acetaminophen toxicity result in AST & ALT LEVELS > 50 times normal.Note:- check level of albumin , prothrombin time, clotting factors , etc.
Other test if needed:- pancreatic enzyme test, kidney function test ,etc.
Instumental diagnosis approch:-
- USG
- C-xray
- CT- scan ( to fine obstruction of pancreatic head , pancreatic cancer ,etc)
- MRI
- Cholangioscopic biopsy
Management of jaundice
In case of neonates severe case of jaundice occurs because liver is not functioning well because not mature and not producing enough UGT enzyme so unconjugated bilirubin level increases. if not treated in time then it leads to kernicterus( damage of basal ganglion). So treat with phototherapy( it makes unconjugated bilirubin to conjugated by modifying UGT enzyme and excreated from urine.Life style modifications:- manage stress, regular exercise maintain hygenic wayof living, avoid iv drugs using, alcohol, smoking,etc.
Dite changes:-
less fatty food , fried and salty too, junk food, try to eat green leafy vegetables and fruits( papaya, apple, orange,etc), take enough leamon ,raddish , neem leaf , sugarcane juice etc.
Medical treatment:-
Treat underlying causes of liver diseases , symptomatic treatment , can use ursodeoxycholic acid in order to reduce itching. etc.
Surgical treatment:- splenectomy, cholecystectomy, surgical removal of gall stones , ichiness may help by draining the gallbladder etc.
Note:- New born baby may develop physiological jaundice first 2 days and then gradually resolve its own.Yellowish skin may occur but not jaundice in case of eating beta carotene rich food and medications like rifampin.

Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, please let me know