What is prostate cancer?
- The foremost common form of cancer in men and second most frequent reason for cancer-related death in men .
- A malignant (cancerous) neoplasm that begins within the ductless gland
- Some prostate cancers grow terribly slowly and should not cause issues for years
- prostate cancer is somewhat uncommon in this several men with advanced cancer answer treatment.
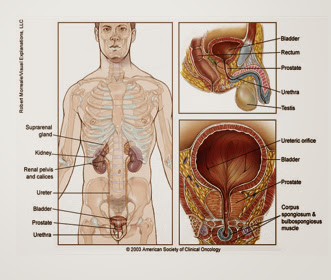
What is prostate gland?
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized secretory gland located behind the base of the penis, in front of the rectum and below the Urinary bladder .
It surrounds the urethra, which is tube- like channel that carries urine from bladder and semen through the penis.
The main function of the prostate gland is to produce seminal fluid, the seminal fluid in semen that protects, supports, and helps to transport sperm.
Risk Factor/ cause for prostate cancer
- Increasing Age
- Racism /ethnicity
- Positive Family history
- Dietary condition
- Hormones
- Exposure to cancer causing chemical
Prostate Cancer and Early Detection
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
- Digital rectal examination (DRE)
Prostate cancer symptoms
- Increase Frequency of urination, or weak or interrupted urine passage.
- Pain or burning sensation during Micturition or blood in the urine(hematuria)
- Urge to urinate frequently at night(urgency)
- Different symptoms if the cancer has spread to other structure: back pain, loss of weight, fatigue etc.
- Sometimes asymptomatic, many people with prostate cancer do not show any symptoms, or symptoms could be similar with symptoms of other disease conditions.
prostate cancer screening include:
- PSA
- DRE
- Biopsy is confirmatory test
- Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)
- Imaging tests may determine if the cancer has spread to other places.
prostate cancer stages
- Staging is a way of describing a tumor, such as the depth of the tumor and where it has spread.
- Staging is the foremost important tool doctors have to determine a patient’s prognosis of cancer.
- Staging is described by the TNM classification:
T stands for “ size of the Tumor”,
N stands for Nodes - whether tumor has spread to nearest lymph Nodes.
M stands for Metastasis - Tumor spread to the other organs such as the liver or lungs etc).
- Another tumor staging system assigns English alphabets (A,B,C,D) to Describe the Tumor.
- Type of prostate cancer treatment is depends on the stage of the Tumor.
Prostate cancer grading
- Grade describes how much tumor cells look like to normal cells
- The grade of the Tumor may help to the doctor predict how quickly the tumor will be spread.
- The Gleason System is the most common grading system of Tumor and its describes the cell patterns seen under the light microscope.
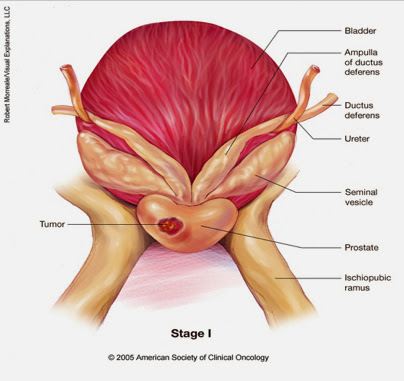
Stage I (stage A) Prostate cancer
Stage I prostate cancer is found only in the prostate gland and which is usually grows slowly.
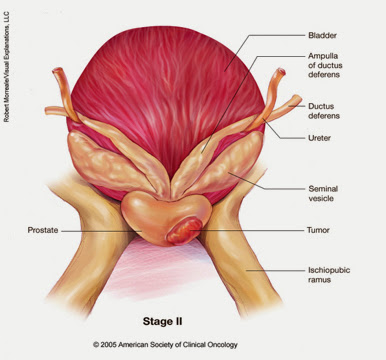
Stage II(stage B) Prostate cancer
Stage II prostate tumor has not yet spread behind the prostate gland, but which involves more than 1 part of the prostate gland, and which may be t grow more rapidly.
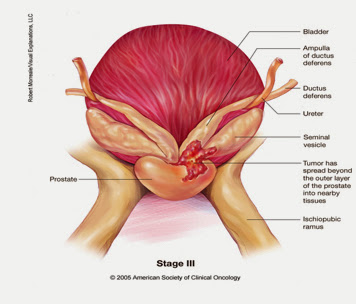
Stage III(stage C) Prostate cancer
Stage III prostate cancer has spread behind the outer layer of the prostate gland into nearby tissues structure or to the seminal vesicles.
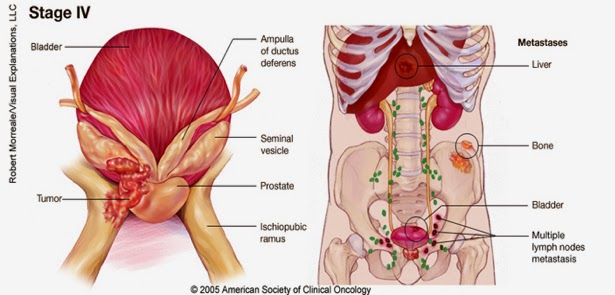
Stage IV(stage D) Prostate cancer
Stage IV prostate tumor has spread to other areas of the human body such as the urinary bladder, rectum, bone, liver, lungs, or lymph nodes etc.
prostate cancer treatment option
- Treatment option of prostate cancer depends on stage of Tumor
- More than 1 treatment may be used in prostate cancer
- Surveillance of prostate cancer (watchful and waiting condition) for some early stage of tumor.
- Surgery of prostate Cancers
- Radiation therapy may used
- Hormone therapy
- Chemotherapy also useful
Prostate Cancer treatment - with watchful and waiting condition:
- Is A way to monitor early stage, slowly growing prostate cancer
- Appropriate when treating prostate cancer could cause more discomfort than the disease itself.
- Mostly used in elderly men or men who are unwell from other kinds of illnesses
- Prostate cancer Treatment begins when the tumor shows signs of growing or spreading to other places.
Prostate Cancer Surgery
- Surgery is used to try to cure prostate tumor before it spreads outside the prostate gland.
- During surgery, the prostate gland and nearby lymph nodes are usually removed
- The side effect of surgery include Urinary incontinence and sexual discomfort.Which are treatable side effects.
- Cryosurgery is destroying tumor cells by freezing it is still not in practice.
Radiation therapy for Prostate Cancer treatment
- High-energy x-rays or other radioactive particles are used to destroy tumor cells
- It is Used to cure tumor or control symptoms
- External-beam: outside the body
- Brachytherapy: the insertion of radioactive pellets into the prostate gland.
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): it is small beams of radiation are aimed at the tumor from many angles.
- Side effects of radiation therapy may include rash and dryness, reddened and discolored skin.
Hormone therapy for prostate cancer
- we reduce level of male sex hormones in our body to slow growth of prostate gland cancer.
- It is used to treat prostate cancer that has grown after surgery and radiation therapy and also used to shrink large tumors prior to surgery & radiation therapy
- Hormone therapy can have a variety of possible side effects.
Chemotherapy for prostate cancer
- Drugs which are used to kill tumor cells
- There is No standard chemotherapy for prostate cancer treatment.
- Mitoxantrone (Novantrone) and docetaxel (Taxotere). both of them are used in men with prostate tumor that is resistant to hormonal therapy.
- Paclitaxel (Taxol), estramustine (Estracyte), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), and cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) have shown promise in treating advanced level of prostate gland cancer.
Prostate cancer survival rate:
5 yrs survival rate with regional stages of prostate cancer is about 100%.

Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, please let me know